ASEAN Shared Mobility Growth Opportunities
ASEAN Shared Mobility Growth Opportunities
Transformative Mega Trends Lead to Automotive Electrification and the Innovation of Super Shared Mobility Applications
09-Nov-2021
Asia Pacific
Description
The study assesses the key shared mobility trends in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), covering Cambodia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. Key shared mobility activities discussed in the study include car sharing, eHailing, ride sharing, demand-responsive transit, and micro mobility.
In 2020, affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, social distancing and country-wide lockdowns in Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines and Thailand reduced the demand of eHailing services. The corresponding governments restricted the social and business activities of residents. eHailing business was affected, and this trend will continue in the short term.
Market oligopoly leads to high entry barriers for potential new entrants. Grab and Gojek own the largest fleet and subscriber base in ASEAN. Hence, the eHailing market entry barriers are relatively high. In particular, Grab has expanded its business to most ASEAN countries. In addition, Grab integrates food delivery and shared mobility service in its apps; this increases the usage rate and reliability of users. At the same time, it reduces market opportunities for other competitors.
Although private vehicle ownerships are relatively high in some ASEAN countries, eHailing is in demand in major capital cities. Capital cities, such as Bangkok, Jakarta, and Kuala Lumpur, have heavy traffic and high vehicle flow. Residents face parking difficulties and high parking rates, such as in work spaces and commercial buildings (long parking time). eHailing helps overcome these drawbacks.
Car sharing is a relatively new shared mobility solution in ASEAN. Key adoption countries include Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand. The market is nascent and will continue to grow.
The study profiles top 10 shared mobility trends in ASEAN. Each shared mobility trend includes snapshots of key value proposition, profiles of key industry participants, and relevant case study of the trend.
In addition, the study also covers key growth drivers and growth restraints of the market, and identifies three growth opportunities.
Author: Ming Lih Chan
RESEARCH: INFOGRAPHIC
This infographic presents a brief overview of the research, and highlights the key topics discussed in it.Click image to view it in full size
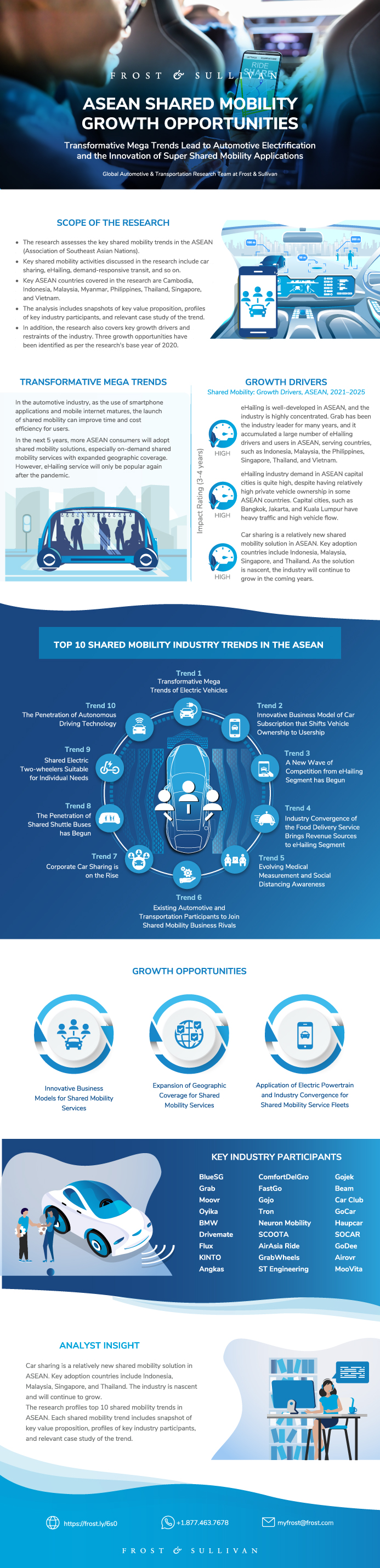
Table of Contents
Why Is It Increasingly Difficult to Grow?
The Strategic Imperative 8™
The Impact of Top Three Strategic Imperatives on ASEAN’s Shared Mobility
Growth Opportunities Fuel the Growth Pipeline Engine™
Shared Mobility Overview in ASEAN
Shared Mobility Segmentation
Growth Drivers in ASEAN’s Shared Mobility
Growth Restraints in ASEAN’s Shared Mobility
ASEAN Shared Mobility Trend 1—Transformative Mega Trends of Electric Vehicles
Key Industry Participants—Transformative Mega Trends of Electric Vehicles
ASEAN Shared Mobility Trend 2—Innovative Business Model of Car Subscription that Shifts Vehicle Ownership to Usership
Key Industry Participants—Innovative Business Model of Car Subscription that Shifts Vehicle Ownership to Usership
ASEAN Shared Mobility Trend 3—A New Wave of Competition from eHailing Market has Begun
Key Industry Participants—A New Wave of Competition from eHailing Market has Begun
ASEAN Shared Mobility Trend 4—Industry Convergence of the Food Delivery Service Brings Revenue Sources to eHailing Market
Key Industry Participants—Industry Convergence of the Food Delivery Service Brings Revenue Sources to eHailing Market
ASEAN Shared Mobility Trend 5—Evolving Medical Measurement and Social Distancing Awareness
Key Industry Participants—Evolving Medical Measurement and Social Distancing Awareness
ASEAN Shared Mobility Trend 6—Existing Automotive and Transportation Participants to Join Shared Mobility Business Rivals
Key Industry Participants—Existing Automotive and Transportation Participants to Join Shared Mobility Business Rivals
ASEAN Shared Mobility Trend 7—Corporate Car Sharing is on the Rise
Key Industry Participants—Corporate Car Sharing is on the Rise
ASEAN Shared Mobility Trend 8—The Penetration of Shared Shuttle Buses has Begun
Key Industry Participants—The Penetration of Shared Shuttle Buses has Begun
ASEAN Shared Mobility Trend 9—Shared Electric Two Wheelers Suitable for Individual Needs
Key Industry Participants—Shared Electric Two Wheelers Suitable for Individual Needs
ASEAN Shared Mobility Trend 10—The Penetration of Autonomous Driving Technology
Key Industry Participants—The Penetration of Autonomous Driving Technology
Growth Opportunity 1—Innovative Business Models for Shared Mobility Services
Growth Opportunity 1—Innovative Business Models for Shared Mobility Services (continued)
Growth Opportunity 2—Expansion of Geographic Coverage for Shared Mobility Services
Growth Opportunity 2—Expansion of Geographic Coverage for Shared Mobility Services (continued)
Growth Opportunity 3—Application of Electric Powertrain and Industry Convergence for Shared Mobility Service Fleets
Growth Opportunity 3—Application of Electric Powertrain and Industry Convergence for Shared Mobility Service Fleets (continued)
Table of Acronyms Used
List of Exhibits
List of Exhibits (continued)
List of Exhibits (continued)
Legal Disclaimer
| No Index | No |
|---|---|
| Podcast | No |
| Author | Ming Lih Chan |
| Industries | Automotive |
| WIP Number | PB89-01-00-00-00 |
| Is Prebook | No |
| GPS Codes | 9673-A6,9800-A6,9A57-A6,9AF6-A6 |
 USD
USD GBP
GBP CNY
CNY EUR
EUR INR
INR JPY
JPY MYR
MYR ZAR
ZAR KRW
KRW THB
THB