North America Building Technology Buying Processes and Bid Spec Process Evaluation, 2017
North America Building Technology Buying Processes and Bid Spec Process Evaluation, 2017
Adopting a Traditional Approach Rather than a Collaborative Approach to Project Management is the Main Reason for Sub-par Project Efficiency
31-Aug-2018
North America
$4,950.00
Special Price $3,712.50 save 25 %
Description
This research service offers in-depth understanding of the practices, challenges, process influencers, and opportunities pertaining to intelligent building (IB) design and implementation. The concept of IBDI processes was examined from the perspectives of building owners, occupants, vendors, service providers, and industry associations. It was found that the lack of efficient design and communication among the key stakeholders was the major challenge encountered by companies during the design and implementation of IB. Adopting a traditional approach rather than a collaborative approach to project management is the main reason for sub-par project efficiency and limited technology advancements. Traditional design and implementation processes are inadequate to meet the needs of dynamic entities such as IBs. It was noticed that only 30 percent of respondents followed best practices during the implementation of the project. Therefore, to improve the design and implementation processes, traditional silo-based approaches need to be abandoned in favor of a strategic and holistic view of the projects, beyond first costs. An integrated approach will help dissolve the barriers that isolate the design and implementation stages by bringing together all participants and their various knowledge and skills.
In addition to that, it was seen that architects, design and build contractors, and technology consultants are the top three partners that influence the design specifications. The level of influence of these three is higher in new construction activities than renovation and retrofit projects. In terms of technology, lighting and HVAC is anticipated to be the leading technologies for future renovations, tenant fit outs, and new installations.
Research Highlights
The key focus areas of the project include the following:
- Evaluating the benefits of adopting proper design and implementation practices
- Understanding various design processes currently in use and the ways to improve their adoption
- Addressing issues and challenges stated by value chain participants and determining ways to mitigate them
- Determining opportunities for collaborations and partnerships to resolve common challenges
Key Conclusions
The study presents the importance and implications of adopting the best design practices and implementation methods that could increase the adoption of the IB technologies and services. Frost & Sullivan hopes these findings will encourage vendors and service providers to consider incorporating IB design elements and implementation measures to create buildings that serve the holistic needs of occupants.
RESEARCH: INFOGRAPHIC
This infographic presents a brief overview of the research, and highlights the key topics discussed in it.Click image to view it in full size
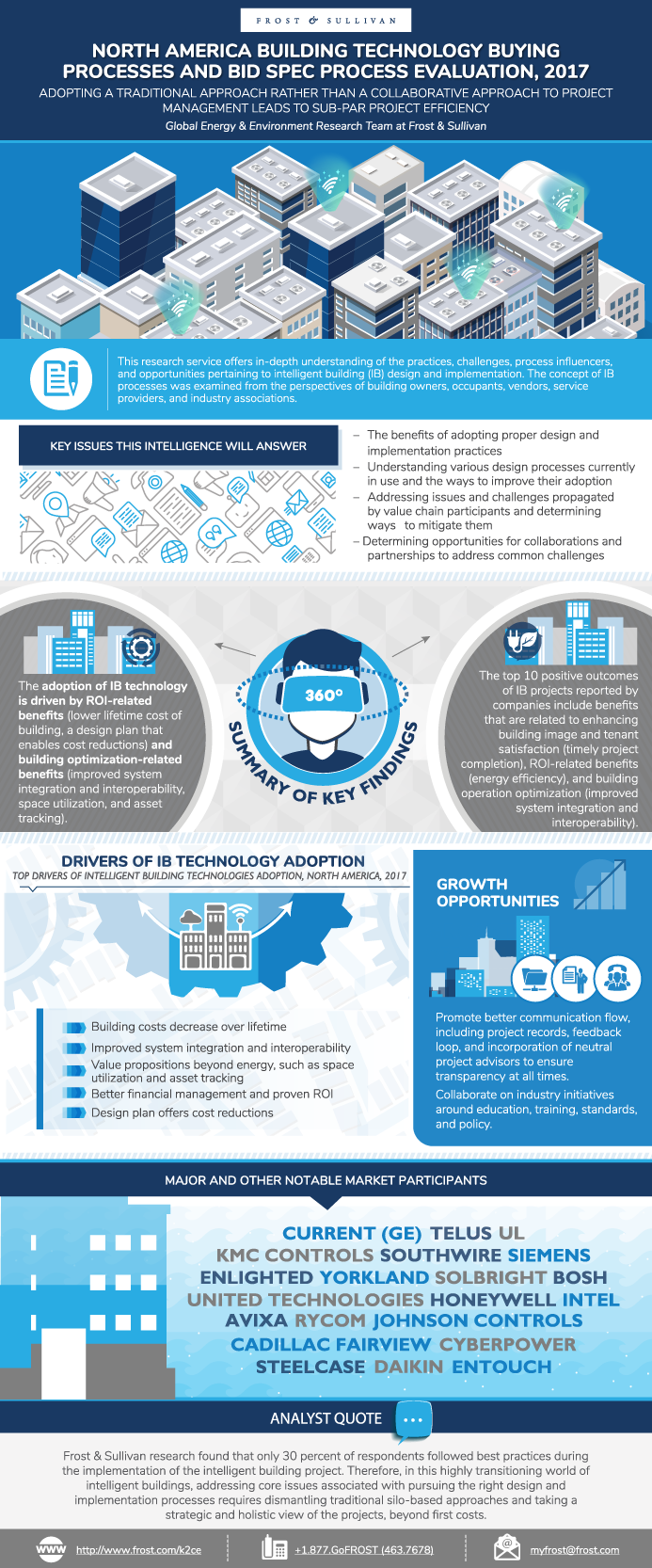
Table of Contents
Research Objectives
Research Methodology
Profile of Respondents—Country and Firm Size
Profile of Respondents—Type of Organization
Profile of Respondents—Job Titles
Summary of Key Findings
Drivers of IB Technology Adoption
Drivers of IB Technology Adoption (continued)
Drivers of IB Technology Adoption (continued)
Drivers of IB Technology Adoption (continued)
Top 10 Positive Outcomes of IB Projects
IB Project Experience—Overall Outcome
IB Project Experience—Overall Outcome (continued)
IB Project Experience—Overall Outcome (continued)
IB Project Experience—Overall Outcome (continued)
IB Project Experience—Overall Outcome (continued)
IB Project Experience—Overall Outcome (continued)
Reasons for IB Project Success
Top 5 Negative Practices and Outcomes of IB Projects
IB Project Experience—Negative Practices and Outcomes
IB Project Experience—Negative Practices and Outcomes (continued)
IB Project Experience—Negative Practices and Outcomes (continued)
Reasons for Sub-optimal IB Project Outcome
Reasons for Sub-optimal IB Project Outcome (continued)
Reasons for Sub-optimal IB Project Outcome (continued)
Reasons for Sub-optimal IB Project Outcome (continued)
Top Positive and Negative IB Design Practices and Outcomes
IB Project Experience—IB Design Practices and Outcomes
IB Project Experience—IB Design Practices and Outcomes (continued)
IB Project Experience—IB Design Practices and Outcomes (continued)
Other Positive and Negative IB Project Practices and Outcomes
IB Project Experience—Other Practices and Outcomes
IB Project Experience—Other Practices and Outcomes (continued)
IB Project Experience—Other Practices and Outcomes (continued)
Top 10 IB Design and Implementation Practices
Perceived Value of Design and Implementation Practices
Perceived Value of Design and Implementation Practices (continued)
Perceived Value of Design and Implementation Practices (continued)
Perceived Value of Design and Implementation Practices (continued)
Perceived Value of Design and Implementation Practices (continued)
Perceived Value of Design and Implementation Practices (continued)
IB Best Practice Orientation Segments
IB Best Practice Orientation Segments (continued)
Summary of Key Differences between IB Best Practice Segments
Summary of Key Differences between Owners and IBDI Project Partners
Sectors and Industries
Number of IB Design Projects—Last Two Years
Expected Trend in the Number of IB Projects
Involvement in Various Building Project Phases
Involvement in Various Building Project Phases (continued)
Involvement in Various Building Project Phases (continued)
Project Type and Region
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies: Past and Future
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies: Past and Future (continued)
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies Included
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies Included (continued)
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies Included (continued)
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies Included (continued)
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies to be Included in the Next Two Years
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies to be Included in the Next Two Years (continued)
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies to be Included in the Next Two Years (continued)
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies to be Included in the Next Two Years (continued)
Most Problematic or Challenging Technologies to Implement
Most Problematic or Challenging Technologies to Implement (continued)
Most Problematic or Challenging Technologies to Implement (continued)
Most Problematic or Challenging Technologies to Implement (continued)
Most Problematic or Challenging Technologies to Implement (continued)
Most Problematic or Challenging Technologies to Implement (continued)
Why Technologies are Difficult to Implement
Why Technologies are Difficult to Implement (continued)
Why Technologies are Difficult to Implement (continued)
Why Technologies are Difficult to Implement (continued)
Why Technologies are Difficult to Implement (continued)
Why Technologies are Difficult to Implement (continued)
Why Technologies are Difficult to Implement (continued)
Measures to Prevent IB Technology Implementation Problems
Measures to Prevent IB Technology Implementation Problems (continued)
Measures to Prevent IB Technology Implementation Problems (continued)
Measures to Prevent IB Technology Implementation Problems (continued)
Technology Implementation Aspects
Technology Implementation Aspects (continued)
Technology Implementation Aspects (continued)
Involvement of Parties in IB Specification Development
Involvement of Parties in IB Specification Development (continued)
Involvement of Parties in IB Specification Development (continued)
Influence of Parties in the Specification of IB Solutions
Influence of Parties in the Specification of IB Solutions (continued)
Influence of Parties in the Specification of IB Solutions (continued)
Perceived Trends in the Influence of Parties in New Construction
Perceived Trends in the Influence of Parties in Major Renovations
Perceived Trends in the Influence of Parties in Fit Outs and Retrofits
Building Certifications that are Considered Important
Building Certifications that are Considered Important (continued)
Building Certifications that are Considered Important (continued)
End-Customer Education on IB Design/ Implementation—Some Methods and Topics
End-Customer Education on IB Design/ Implementation—Some Methods and Topics (continued)
End-Customer Education on IB Design/ Implementation—Some Methods and Topics (continued)
End-Customer Education on IB Design/ Implementation—Some Methods and Topics (continued)
IB Best Practice Orientation Segments
Drivers of IB Technology Adoption
IB Project Experience—Overall Outcome
IB Project Experience—Overall Outcome (continued)
IB Project Experience—Negative Practices and Outcomes
IB Project Experience—IB Design Practices and Outcomes
IB Project Experience—Other Practices and Outcomes
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies Included
Profile of Projects—Types of Technologies Included (continued)
Most Problematic or Challenging Technologies to Implement
Most Problematic or Challenging Technologies to Implement (continued)
Perceived Value of Design and Implementation Practices
Perceived Value of Design and Implementation Practices (continued)
Legal Disclaimer
List of Exhibits
List of Exhibits (continued)
List of Exhibits (continued)
List of Exhibits (continued)
The Frost & Sullivan Story
Value Proposition—Future of Your Company & Career
Global Perspective
Industry Convergence
360º Research Perspective
Implementation Excellence
Our Blue Ocean Strategy
Popular Topics
Research Highlights
The key focus areas of the project include the following:
- Evaluating the benefits of adopting proper design and implementation practices
- Understand
| No Index | No |
|---|---|
| Podcast | No |
| Author | Pratik Paul |
| Industries | Environment |
| WIP Number | K2CE-01-00-00-00 |
| Is Prebook | No |
| GPS Codes | 9343-A4,GETE |
 USD
USD GBP
GBP CNY
CNY EUR
EUR INR
INR JPY
JPY MYR
MYR ZAR
ZAR KRW
KRW THB
THB