Emerging Landscape of Targeted Protein Degradation Therapeutics
Emerging Landscape of Targeted Protein Degradation Therapeutics
Rapid Technology Advances Bolster a Robust Therapeutic Pipeline
29-Jun-2023
Global
Description
This Frost & Sullivan research report provides an in-depth analysis of the emerging targeted protein degradation (TPD) space. TPD strategies enable treating various diseases not yet treatable via conventional approaches by attacking disease-causing proteins in a controlled manner, thus reducing the risk of side effects.
It is estimated that 80% of a cell’s proteome cannot be targeted via traditional approaches such as small molecule inhibitors, ASO, or monoclonal antibodies, which has led to the development of TPD approaches. Indeed, TPD has advanced enormously in the last two decades, and PROTACs have emerged as the most common protein degrader researched until now. As new technologies emerge, several types of protein degraders have been developed.
Two main types exist: intracellular and extracellular degraders. Until now, intracellular protein degraders have been the most extensively studied. These degrade intracellular proteins by leveraging the ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation pathway, but an estimated 40% of genes encoding extracellular and membrane-associated proteins cannot be targeted by intracellular protein degraders, leading to the development of extracellular protein degradation.
Increased private and public funding is an important factor driving the growth of targeted protein degradation technology. This report includes an analysis of funding trends in the TPD space.
This report discusses the different types of extracellular and intracellular protein degraders and R&D focus areas; it analyses the applicability of different degraders across various diseases and identifies their clinical translation and related key players. Finally, Frost & Sullivan has identified four growth opportunities for TPD that could potentially transform the market.
Questions that this report seeks to answer include:
1. What are the key drivers or challenges for TPD development?
2. How do the private funding and partnership landscapes look for TPD?
3. Who are the key industry participants developing targeted protein degraders?
4. What are the R&D trends emerging across TPD that could further shape the development of protein degraders?
RESEARCH: INFOGRAPHIC
This infographic presents a brief overview of the research, and highlights the key topics discussed in it.Click image to view it in full size
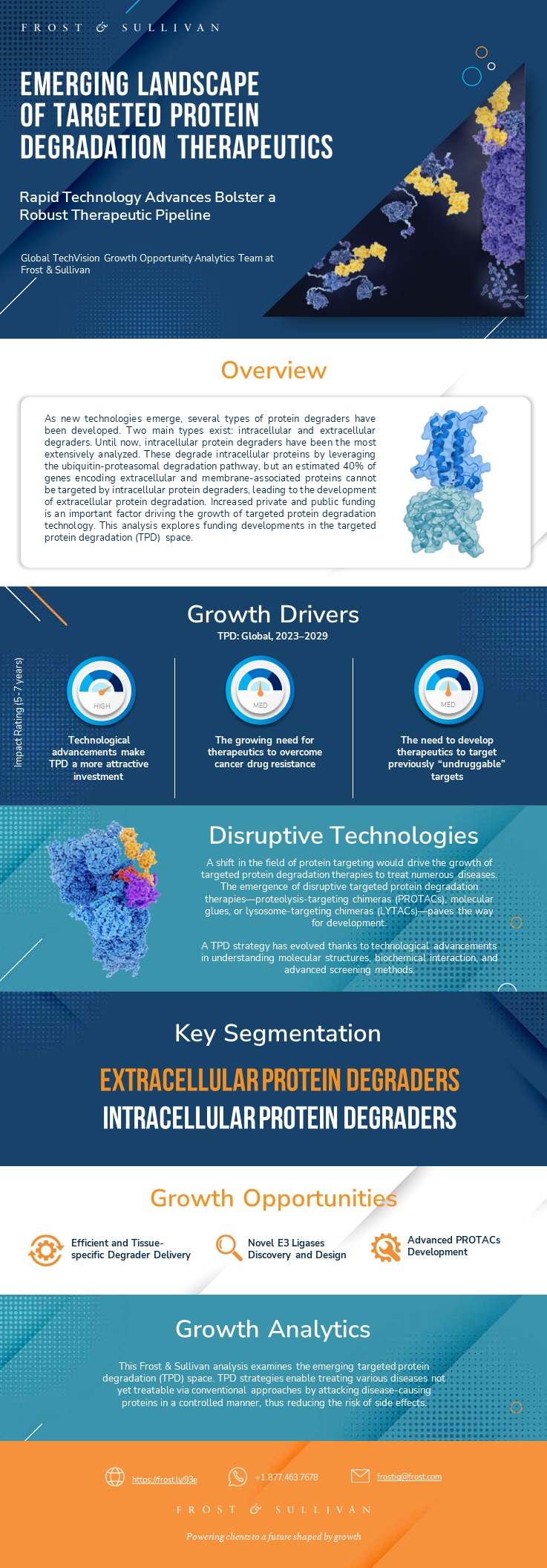
Table of Contents
Why Is It Increasingly Difficult to Grow?
The Strategic Imperative 8™
The Impact of the Top 3 Strategic Imperatives on the Targeted Protein Degradation Industry
Growth Opportunities Fuel the Growth Pipeline Engine™
Research Methodology
Introduction
Growth Drivers
Growth Driver Analysis
Growth Driver Analysis (continued)
Growth Restraints
Growth Restraints Analysis
Scope of Analysis
Segmentation
The Need for Targeted Protein Degraders
TPD—Evolution and Clinical aspect
Intracellular Targeted Protein Degraders in Clinical Development
Intracellular Targeted Protein Degraders—PROTACs
Emerging Intracellular Targeted Protein Degraders
Emerging Intracellular Targeted Protein Degraders (continued)
Innovation Spotlight—Intracellular Protein Degradation
Development of Extracellular Protein Degradation Therapeutics
Challenges for Extracellular Protein Degrader Development
Extracellular Protein Degradation Approaches
Emerging Classes of Extracellular Protein Degraders
Emerging Classes of Extracellular Protein Degraders (continued)
Innovation Spotlight—Extracellular Protein Degradation
Key Differences Between Extracellular and Intracellular Protein Targeting
Targeted Protein Degradation Technology Snapshot
Targeted Protein Degradation Technology Snapshot (continued)
R&D Innovation Trends
R&D Innovation Trends (continued)
Protein Degraders in Healthcare and Beyond
Protein Degraders across Different Disease Areas
Protein Degraders across Different Disease Areas (continued)
Key Players and Therapeutics Areas of Focus
Key Players and Therapeutics Areas of Focus (continued)
Protein Degraders Innovation Landscape
Public and Private Funding for TPD Therapy Development
Public and Private Funding for TPD Therapy Development (continued)
Public and Private Funding for TPD Therapy Development (continued)
Partnership Landscape of Biopharma Companies in TPD Therapeutics Development
Partnership Landscape of Biopharma Companies in TPD Therapeutics Development (continued)
Partnership Landscape of Biopharma Companies in TPD Therapeutics Development (continued)
TPD Companies’ Partnerships for Developing TPD Therapeutics
Growth Opportunity 1: Efficient and Tissue-specific Degrader Delivery
Growth Opportunity 1: Efficient and Tissue-specific Degrader Delivery (continued)
Growth Opportunity 2: Novel E3 Ligases Discovery and Design
Growth Opportunity 2: Novel E3 Ligases Discovery and Design (continued)
Growth Opportunity 3: Advanced PROTACs Development
Growth Opportunity 3: Advanced PROTACs Development (continued)
Growth Opportunity 4: Research and Product Development Partnerships to Develop Next-gen TPD Therapeutics
Growth Opportunity 4: Research and Product Development Partnerships to Develop Next-gen TPD Therapeutics (continued)
Appendix
Appendix
Your Next Steps
Why Frost, Why Now?
Legal Disclaimer
Popular Topics
| Author | Priyanka Jain |
|---|---|
| Industries | Healthcare |
| No Index | No |
| Is Prebook | No |
| Podcast | No |
| WIP Number | DAA6-01-00-00-00 |
 USD
USD GBP
GBP CNY
CNY EUR
EUR INR
INR JPY
JPY MYR
MYR ZAR
ZAR KRW
KRW THB
THB